Understanding Office Hysteroscopy: A Comprehensive Guide

Office hysteroscopy has emerged as an invaluable diagnostic and therapeutic tool in the world of gynecology. Unlike traditional surgical methods, this minimally invasive procedure allows healthcare providers to examine the interior of the uterus without needing general anesthesia or extensive recovery time. In this article, we will dive deep into what office hysteroscopy entails, its advantages, procedures, possible complications, and much more to provide a holistic view of this critical medical practice.
What is Office Hysteroscopy?
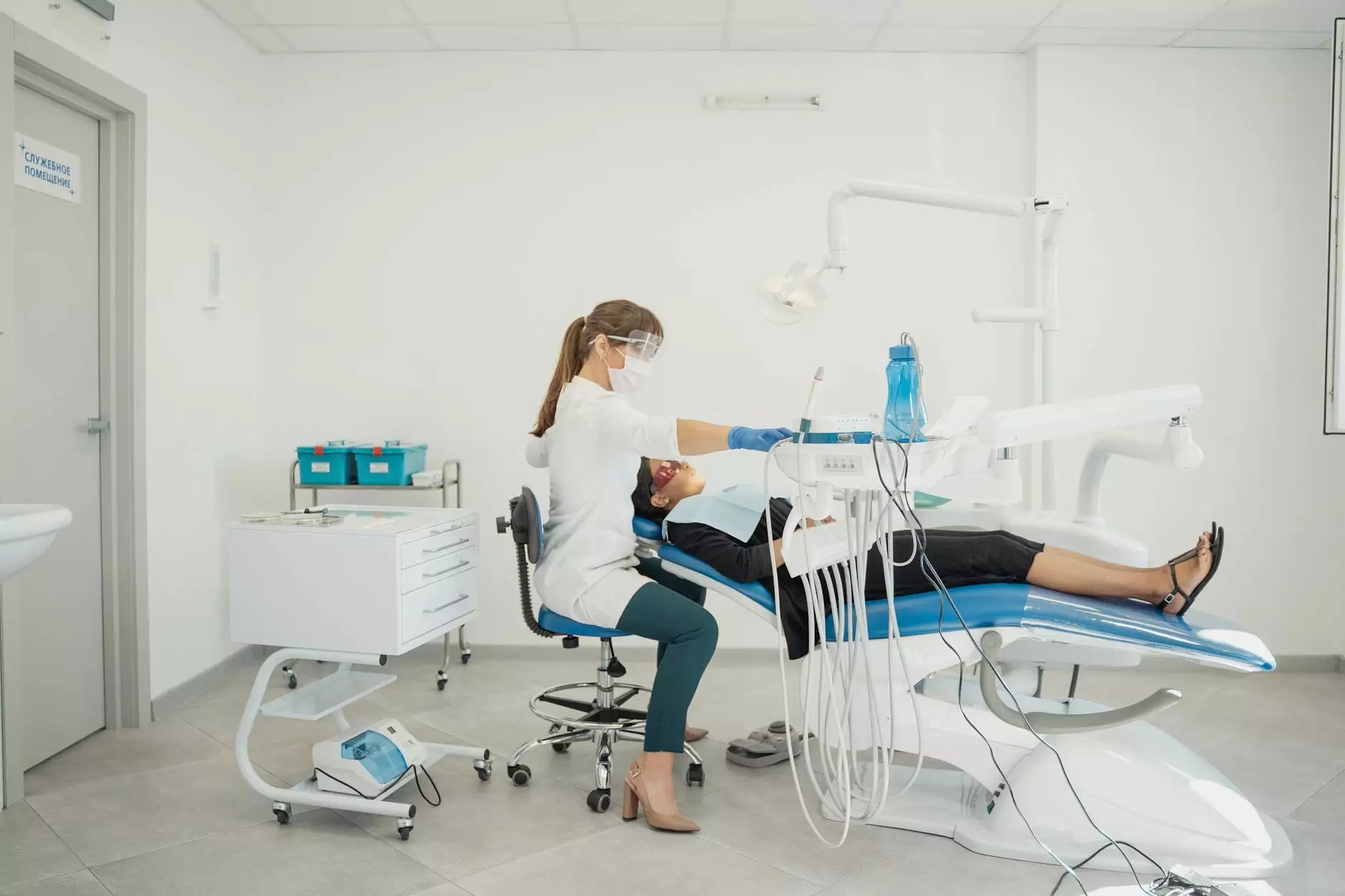
Office hysteroscopy is a medical procedure that involves the use of a hysteroscope—a thin, lighted tube that is inserted through the cervix into the uterus. This enables the physician to visualize the internal structures of the uterus, including the uterine lining, and identify any abnormalities or issues.
How is Office Hysteroscopy Performed?
The procedure typically follows these steps:
- Preparation: Patients are usually advised to come in during the first half of their menstrual cycle to avoid confusion with any potential pregnancy.
- Anesthesia: While general anesthesia is not typically used, some practitioners may offer local anesthesia to minimize discomfort.
- Inserting the Hysteroscope: The doctor inserts the hysteroscope through the cervix and into the uterus. A sterile saline solution may be injected into the uterus to expand it, providing a clearer view.
- Examination: The physician examines the uterine cavity closely for any abnormalities such as polyps, fibroids, or signs of endometrial cancer.
- Treatment (if necessary): If any issues are detected, treatment can often be performed immediately. This might include the removal of polyps or fibroids.
- Recovery: Most women can return to their daily activities shortly after the procedure, though some minor cramping or spotting may occur.
Benefits of Office Hysteroscopy
Office hysteroscopy offers numerous benefits that make it a preferred choice for patients and healthcare providers:
- Minimally Invasive: The procedure does not require large incisions or general anesthesia, making it less stressful for patients.
- Quick Recovery: Patients can generally return to normal activities within 24 hours.
- Early Diagnosis: Quick assessment of uterine health can lead to faster treatment plans.
- Immediate Intervention: Treatment can be performed in the same session, eliminating the need for additional visits.
- Cost-Effective: Fewer hospital visits and less need for anesthesia result in lower overall healthcare costs.